Kinematics of Rotational Motion
Kinematics of Rotational Motion: Overview
This topic covers concepts such as Kinematics of Rotation, Angular Velocity, Angular Velocity of Particle, Angular Velocity of a Rigid Body, Translational and Angular Velocities, Translational and Angular Acceleration, and Relative Angular Velocity.
Important Questions on Kinematics of Rotational Motion
In a uniform circular motion and stands for radius vector, linear velocity and angular velocity respectively. Then which of the following is true?
Assertion: The angular velocity of all the points on the rigid body as seen from any other point on it is the same.
Reason: The distance between any 2 points on the rigid body remains constant.
The angular velocity of a scooter tyre of diameter inches rotates times a second is:
Find the angular velocity of a body rotating with an acceleration of as it completes the revolution after the start.
A body rotates about a fixed axis with an angular acceleration of . Through what angle does it rotate during the time in which its angular velocity increases from to ?
Two particles of equal mass go around a circle of radius under the action of their mutual gravitational attraction. The speed of each partial
with respect to their centre of mass is :
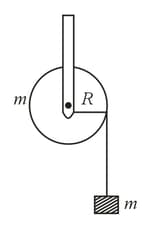
A mass supported by a massless string wound around a uniform solid cylinder of mass and radius If the string does not slip on the cylinder, with what acceleration will the mass fall on release?
If a spherical ball rolls on a table without slipping, the fraction of its total energy associated with rotation is :-
When a ceiling fan is switched off its angular velocity reduces to while it makes rotations. How many more rotation will it make before coming to rest (Assume uniform angular retardation):-
A water fountain on the ground sprinkles water all around it. If the speed of water coming out of the fountain is v, the total area around the fountain that gets wet is
Find the angular velocity of the line joining two particles describing the same circle of radius in the clockwise direction with same speed.
Cotyledons are also called-
A uniform ring of radius is moving on a horizontal surface with speed, then climbs up a ramp of inclination to a height . There is no slipping in the entire motion. Then, is
One end of a rod of length is fixed to a point on the circumference of a wheel of radius The other end is sliding freely along a straight channel passing through the center of the wheel as shown in the figure below. The wheel is rotating with a constant angular velocity (in radian per second) about
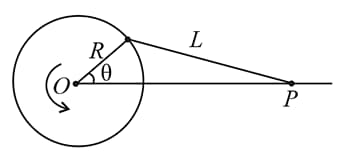
The speed of the sliding end when is
A ball is rolling without slipping in a spherical shallow bowl (radius ) as shown in the figure and is executing simple harmonic motion. If the radius of the ball is doubled, then the time period of oscillation
A wheel which is initially at rest is subjected to a constant angular acceleration about its axis. It rotates through an angle of in time t sec. The increase in angle through which it rotates in the next 2t sec is
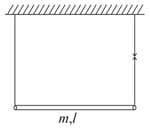
A uniform rod of length and mass is suspended by two vertical inextensible string as shown in figure. Then tension in the left string when right string snaps, is
A particle at rest is to reach an angular velocity of 36 rad in 6 seconds, with a constant angular acceleration. The total angle turned through during this interval is
When a ceiling fan is switched off, its angular velocity reduces to while it makes rotations. How many more rotations will it make before coming to rest? (Assume uniform angular retardation)
A gramophone turn table rotating at slow down uniformly and stops in after the motor is turned off. Its angular acceleration
